About
Our current manufacturing model of ‘take-make-dispose’ is throwing up major economic and environmental challenges. Populations are growing in size and affluence, materials are becoming more scarce, risk to our supply chains is increasing and the cost of waste is higher than ever. Businesses and communities are having to rethink their old assumptions. In shifting towards more 'circular' systems, how can we make use of design thinking that takes into account the unintended consequences and complexity of our 'stuff'?
Our focus during 2014-16 is on the relationship between materials, waste and design. The Great Recovery is now building new networks to explore the issues, investigate innovation gaps and incubate new partnerships in these areas. Supported by Innovate UK and based at Fab Lab London, we are curating a series of practical workshops and events that re-think products, services and systems in order to ‘close the loop’.
We are currently leading a design residency programme focused on bulky waste (mostly furniture items), taking a team of designers to waste and recycling sites and exploring some of the systemic and specific problems that lead to landfill and incineration. We will then create prototypes for new service or product designs that fit with the more circular economy we aspire to.
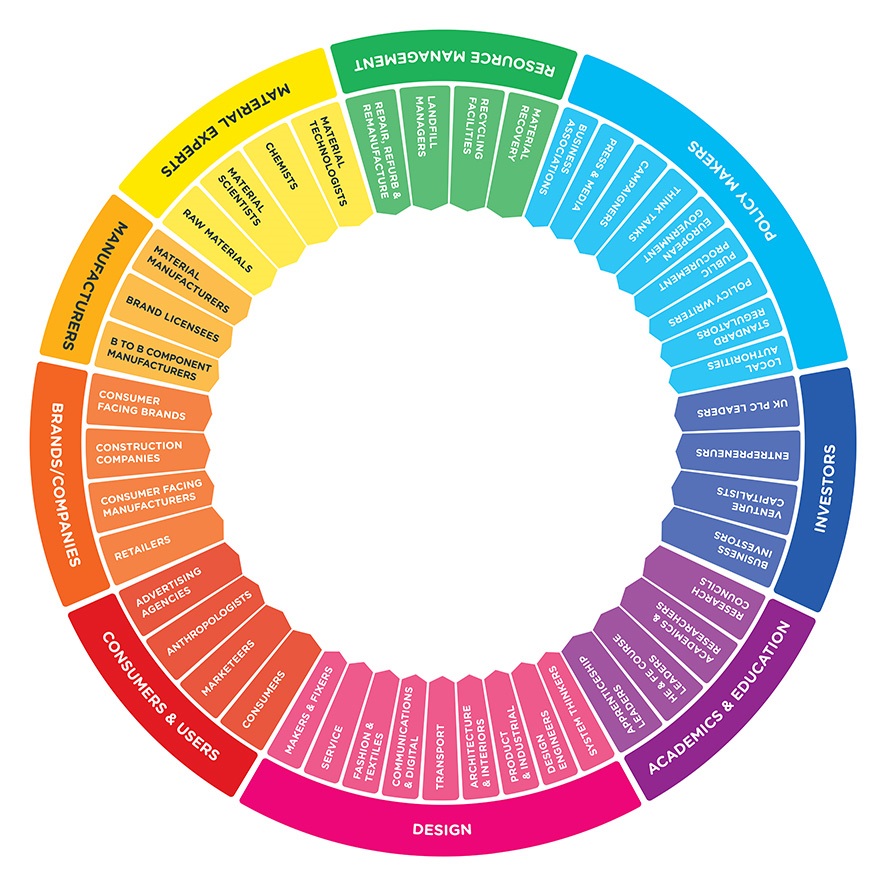
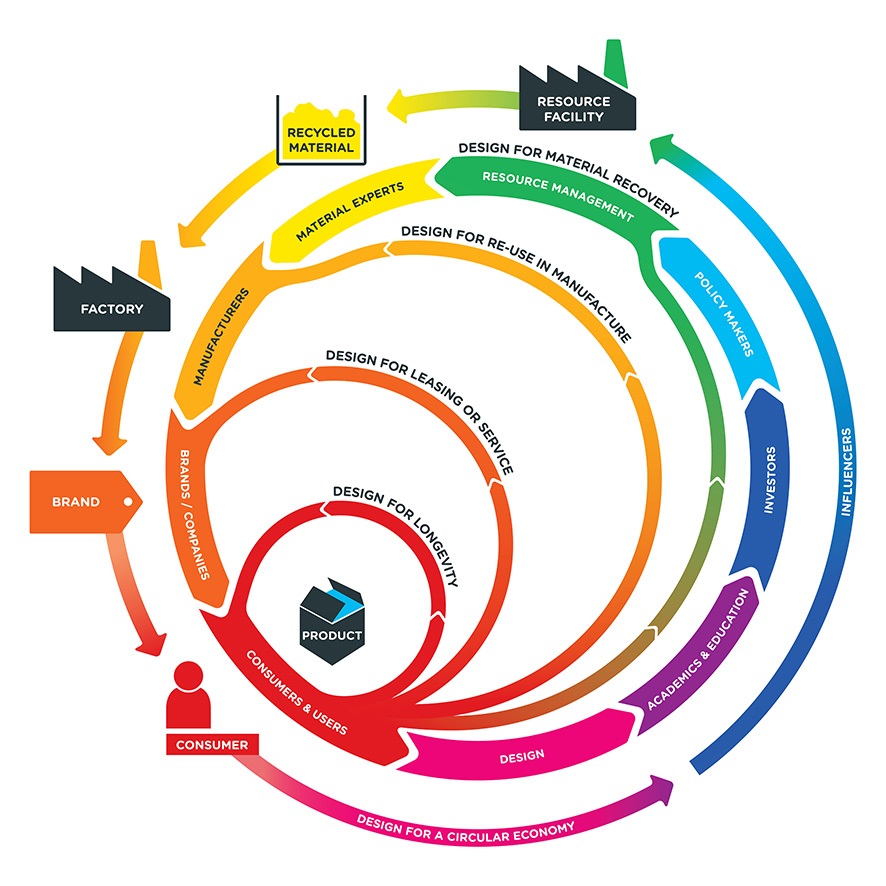
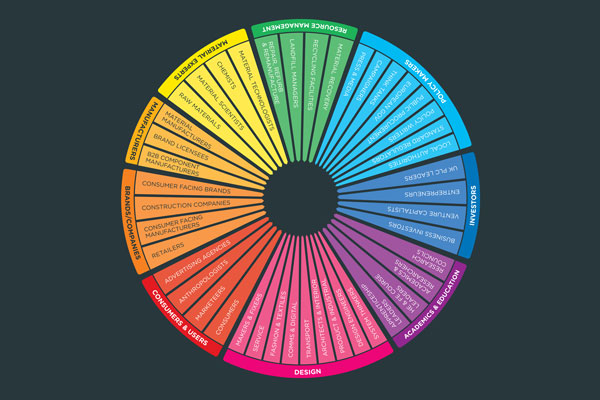
Conclusions from the first stage of the project have shown that we need to:
-
Prepare future generations of designers. Embed circularity in the design education system. Sustainable design must not continue to be left behind or added as a last minute thought.
-
Redesign the brief. Businesses must begin to develop design briefs around new business models that take account of provenance, longevity, impact and end-of-life. They must consider a circular approach.
-
Create access to new spaces that allow collaborative R&D for businesses and their supply chains to test, trial and design around circular principles and the four design models; design for longevity, design for leasing/service, design for re-use in manufacture, and design for material recovery.
-
Laws and accreditation must be fit for circularity. Review the laws that hinder re-manufacturing with used components and that make repair an expensive option.
This RSA project is working in partnership with the Technology Strategy Board, Innovate UK and FabLab London.